What Is Bitcoin and How Does It Work?
It’s 2008, and the world’s financial system is in trouble. people are losing their jobs and savings, Banks are failing, and trust in the financial system has vanished. Everything feels uncertain.
Quick links
The Birth of Bitcoin What Makes Bitcoin Special? The Tech Behind the Magic How Does Bitcoin Really Work? Bitcoin Halving Bitcoin’s Rollercoaster Ride with Regulation Bitcoin as “Digital Gold” How to Buy and Store Bitcoin Conclusion: Bitcoin’s Role
The Birth of Bitcoin
Back in 2009, someone (or a group of people) under the mysterious pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto said, “Hey, let’s create money that doesn’t need banks or governments.” And poof, Bitcoin was born. Okay, it wasn’t that simple, but you get the idea. Bitcoin operates on a peer-to-peer network, meaning you don’t need a mediator like a bank to send or receive it.
Think of it as sending money to your friend, but instead of PayPal or Venmo taking a cut, Bitcoin does the job for (almost) free and without anyone watching.
“Every informed person needs to know about Bitcoin because it might be one of the world’s most important developments.” —Leon Luow, Nobel Peace Prize nominee
What Makes Bitcoin Special?
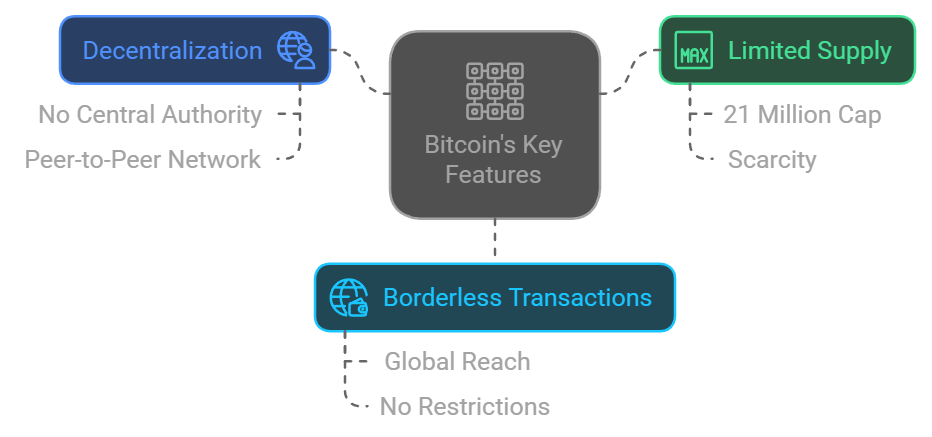
Bitcoin isn’t just digital Monopoly money. Here’s what makes it unique:
- Decentralization
No single person or company controls Bitcoin. It’s like a public park where everyone has a say, but no one owns it. - Limited Supply
There will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins. No printing extra like governments do with fiat currency (looking at you, inflation!). - Borderless Transactions
Whether you’re in New York or Timbuktu, Bitcoin works the same way. No exchange rates, no delays, no drama.
The Tech Behind the Magic: Blockchain
The backbone of Bitcoin is the blockchain, a fancy term for a digital ledger. Imagine a super-organized notebook where every transaction is written down in permanent ink.
Here’s how it works:
- Transactions are grouped into blocks.
- Once a block is full, it gets added to the chain of previous blocks.
- This chain grows continuously, creating a transparent and secure record.
The cool part? Once something’s on the blockchain, it’s nearly impossible to change. No erasing, no white-out, the only way to change something on POW (proof of work) blockchain you have to use “51 Attack” using more then 51% of the whole miners of the world which is impossible in terms of bitcoin.
but ETC Ethereum classic was attacked with several waves in 2019 and 2020 due to lack of hash rate (mining power) in order to do this single person or group should have more then 50% of hash rate. to attack Bitcoin like that you need 384–390 EH/s, it’s impossible to gather mining equipment at first place, and have such an enormous electric power to run those on the second, due to Bitcoin’s decentralization.
“You can’t stop things like Bitcoin. It will be everywhere, and the world will have to readjust. World governments will have to readjust” —John McAfee, Founder of McAfee
How Does Bitcoin Really Work?
Let’s break down the nitty-gritty without frying your brain.
1. Mining
Imagine a digital gold rush. Miners (people with powerful computers) compete to solve complex puzzles. The winner gets to add a block of transactions to the blockchain and earns some fresh Bitcoin as a reward.
2. Proof of Work (PoW)
This is Bitcoin’s way of making sure everyone’s playing fair. The puzzle miners solve isn’t just for fun—it’s a way to secure the network and keep bad actors out.
3. Keys and Wallets
To own Bitcoin, you need a public key (like your crypto email address) and a private key (your super-secret password). Lose the private key, and it’s like losing the key to a treasure chest—your Bitcoin is gone forever.
Bitcoin Halving: A Look at Its History and Impact
A unique aspect of Bitcoin’s design is its halving events. These are programmed reductions in the reward given to miners, happening every four years. The goal is to control inflation and limit Bitcoin’s supply. Here’s a breakdown of the past halving events and how they affected Bitcoin’s price:
What is Bitcoin Halving?
Every 210,000 blocks (approximately every four years), the reward for mining Bitcoin is cut in half. Initially, miners earned 50 BTC per block, but after each halving, this number drops, reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are created.
Bitcoin Halving Events & Price History
Here’s a brief look at the key halvings and the price movements that followed:
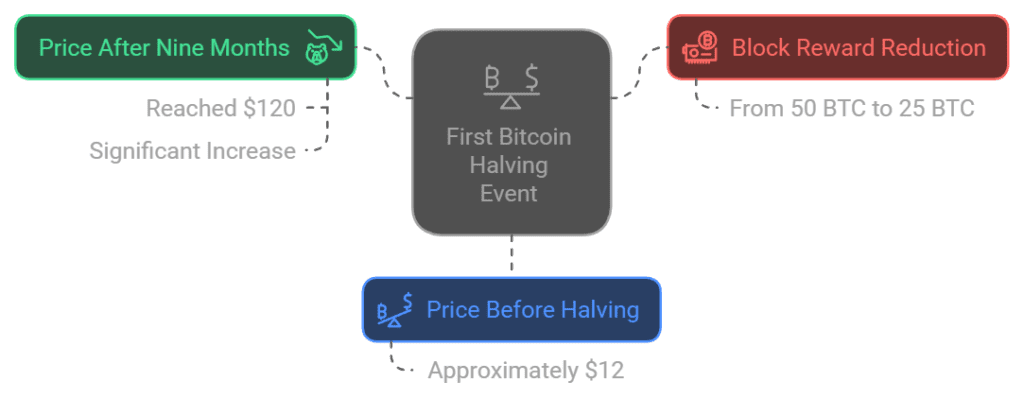
- First Halving – November 28, 2012
- Block Reward: Reduced from 50 BTC to 25 BTC.
- Bitcoin Price Before Halving: Around $12.
- Price Nine Months After Halving: Reached $120, showing a significant increase.
2.Second Halving – July 9, 2016
- Block Reward: Reduced from 25 BTC to 12.5 BTC.
- Price Before Halving: Around $650.
- Price Nine Months Later: Shot up to $1,000 in early 2017, and eventually peaked at nearly $20,000 by the end of 2017.

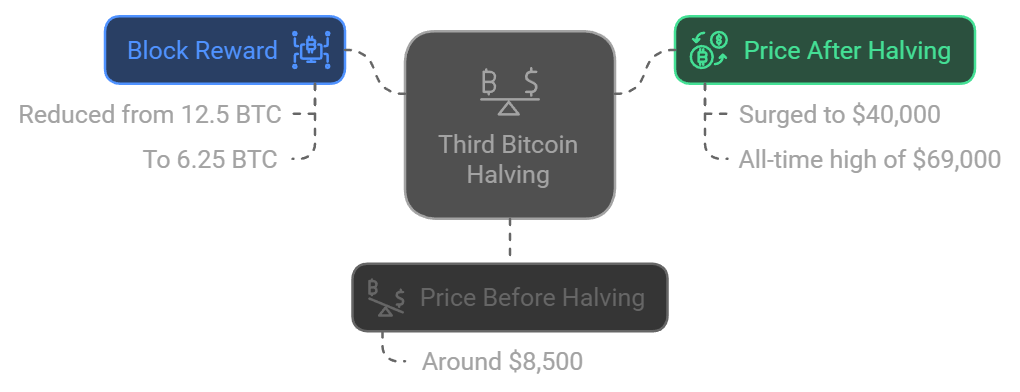
3. Third Halving – May 11, 2020
- Block Reward: Reduced from 12.5 BTC to 6.25 BTC.
- Price Before Halving: Around $8,500.
- Price Nine Months Later: Surged to $40,000 in early 2021, eventually reaching an all-time high of $69,000 in November 2021.
4.Fourth Halving – April 19, 2024
- Block Reward: Reduced from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC.
- Pre-Halving Price: Bitcoin was trading around $62,000 leading up to the event.
- Post-Halving Projections: As of November 25 BTC hovers around $95,000

Bitcoin’s Rollercoaster Ride with Regulation
Bitcoin has had a wild ride navigating government policies. For some, it’s a game-changing innovation; for others, it’s the rebellious teenager of finance that needs strict rules. Let’s explore how different countries have embraced—or rejected—Bitcoin.
China: The Repeated Crackdowns
China’s stance on Bitcoin has been a journey of control.
- 2013: The Early Ban: The government allowed citizens to hold Bitcoin but banned exchanges to curb its growing popularity.
- 2021: Full Prohibition: China took things up a notch, outlawing all crypto transactions and mining. This decision didn’t just affect Bitcoin’s price; it sent miners fleeing to crypto-friendly countries like the U.S. and Kazakhstan. The hash rate fell briefly before recovering globally.
Why the Ban? The Chinese government cited environmental concerns from mining and risks to financial stability. But some speculate it’s about maintaining control over the economy while pushing for its own digital currency, the Digital Yuan.
United States: Regulation in Progress
In the U.S., Bitcoin operates in a gray area, balancing freedom with oversight.
- Federal Policies: Bitcoin is treated as property by the IRS, meaning it’s taxed on gains. The SEC views Bitcoin as a commodity but remains cautious, focusing on investor protection in the broader crypto space.
- State-Level Leadership: Some states, like Wyoming, are rolling out the red carpet with crypto-friendly laws. Others, like New York, have stricter requirements under its BitLicense program.
The Debate: Should Bitcoin remain a decentralized commodity, or does it need stricter oversight to prevent fraud and misuse? While policymakers debate, institutions like BlackRock and Fidelity are exploring Bitcoin ETFs, signaling growing mainstream acceptance.
India: Confusion in Crypto Land
India’s relationship with Bitcoin has been a rollercoaster of bans, legal battles, and uncertainty.
- 2018: Banking Restrictions: The Reserve Bank of India prohibited banks from dealing with crypto companies. This created chaos, cutting off essential financial services for the crypto industry.
- 2020: Ban Overturned: The Supreme Court of India stepped in, lifting the ban and reviving the industry. However, talks of banning “private cryptocurrencies” in favor of a state-backed digital currency continue to cause uncertainty.
Takeaway: India’s regulatory approach remains unclear, but the country’s growing crypto community is pushing for clear and balanced policies.
El Salvador: Bitcoin’s First Official Fan
El Salvador made history by declaring Bitcoin legal tender in 2021.
- Adoption in Action: Citizens can use Bitcoin alongside the U.S. dollar for everyday purchases. The government even introduced the Chivo Wallet and installed Bitcoin ATMs across the country.
- Why Take the Leap? President Nayib Bukele believes Bitcoin can drive financial inclusion in a country where 70% of the population lacks access to traditional banking.
Challenges: The move hasn’t been without critics. Institutions like the IMF warned of economic risks, and adoption rates among locals remain mixed. Still, El Salvador is blazing a trail others might follow.
“The bitcoin system is so perfect that I think it’s gonna be the future. It is the present already in a lot of things, but it’s gonna be way bigger in the future.” — Nayib Bukele in recent interview.
source- Businessinsider .
Europe: Unified but Cautious
The European Union has taken a more uniform approach, focusing on consumer protection and anti-money laundering.
Some countries, like Germany, view Bitcoin as legal private money, allowing individuals to hold and trade it freely (after holding for a year).
The MiCA Regulation (Markets in Crypto Assets) seeks to standardize rules for crypto companies across the bloc, ensuring transparency and security for users.
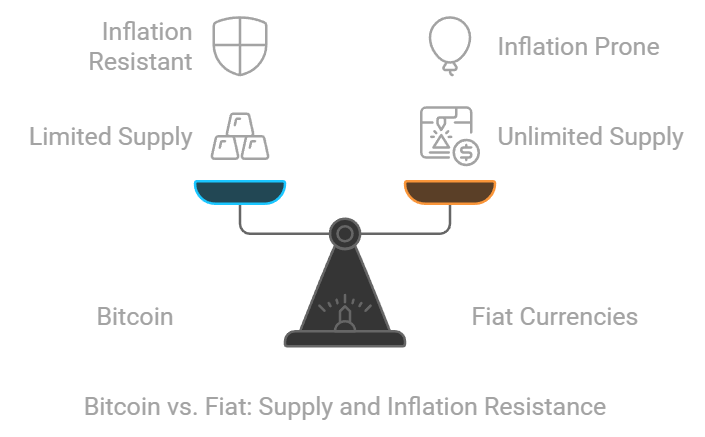
Bitcoin as “Digital Gold”
money that can’t be printed endlessly, Bitcoin is like gold, it’s rare and valuable because only 21 million Bitcoins will ever exist. unlike the dollars or euros we use today.
But Bitcoin not only scarcity. Every transaction is recorded on a public digital book called the blockchain, which anyone can check. This makes it transparent and fair.
In times of economic uncertainty, people turn to Bitcoin, not just as money but as a safe way to store their wealth. Think of it as gold, but transferrable like Fiat currency and scarcer as gold, perfect for the digital world.
A Real-Life Example
Let’s take a trip back to 2013 in Cyprus. The government was in financial trouble and decided to take money from people’s bank accounts to save the economy. people were shocked. Some turned to Bitcoin. Unlike banks, Bitcoin doesn’t let anyone freeze or take your money if you have the private key (think of it as your secret password).
A similar thing happened in Venezuela, where their money became almost worthless because of hyperinflation. People used Bitcoin to buy food and protect their savings.
Bitcoin is more than “digital gold.” For millions, it’s a lifeline in tough times—a way to stay in control when the system feels stacked against them.
Fun Fact: in 2010, someone used 10,000 Bitcoin to buy two pizzas. Today, those coins would be worth 950 millions of dollars! Crazy, right?
How to Buy and Store Bitcoin
Bitcoin can be acquired in several ways, with buying being the most popular:
- Buying from Exchanges: Popular exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken allow you to buy Bitcoin using fiat currencies.
- Mining: Mining is another way to earn Bitcoin, but it has become less accessible due to the high cost of equipment and electricity.
- Earning: You can accept Bitcoin as payment for goods or services.
Storing Bitcoin Safely
- Hardware Wallets: Devices like Ledger or Trezor keep your Bitcoin offline, offering the highest level of security.
- Software Wallets: Apps like Trust wallet or Guarda are convenient i’m using both of them for daily basis, not storing fortune on it though have it as APPs on my smartphone.
- Custodial Wallets: Offered by exchanges, these wallets are managed by third-party services, this is where i store amount which i want to trade.
Bitcoin Price Volatility
Bitcoin’s price has seen dramatic swings since its inception. These swings have been driven by a combination of speculation, regulatory changes, and adoption.
- In 2017, Bitcoin rose from $1,000 to nearly $20,000 before crashing.
- By 2021, it hit an all-time high of $69,000, only to drop significantly again.
This volatility can be challenging for investors but is part of the allure for many.

What the Future Holds for Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s future is bright, but it faces challenges. Here are some key trends:
- Institutional Adoption: More companies, like Tesla and MicroStrategy, are adding Bitcoin to their balance sheets.
- Environmental Concerns: Bitcoin mining consumes a significant amount of energy. However, there is a push for more sustainable practices, with some miners using renewable energy.
- Lightning Network: This Layer-2 solution aims to make Bitcoin transactions faster and cheaper, potentially increasing its use as a daily currency.
Conclusion: Bitcoin’s Role in the Financial Future
Bitcoin isn’t just some techie experiment anymore. Nope, it’s flipping the entire financial system on its head. Think about it. This thing started as a “what if?” from Satoshi Nakamoto (whoever that is) and turned into a multi-billion-dollar beast.
Bitcoin’s kind of like the rebel in the family. It said, “Nah, I’m not playing by your rules” to banks and governments. And guess what? It worked. With just 21 million coins ever, it’s like digital gold but cooler ‘cause you can send it anywhere. No borders. No middlemen. No extra fees, or two to three days transaction nonsense.
“Bitcoin has no top because dollar has no bottom.” – Max Keiser
more about Bitcoin







